✅ RAG Checker
The RAG evaluation system decomposes answers into verifiable units (Claims) based on ER (Expected Response),
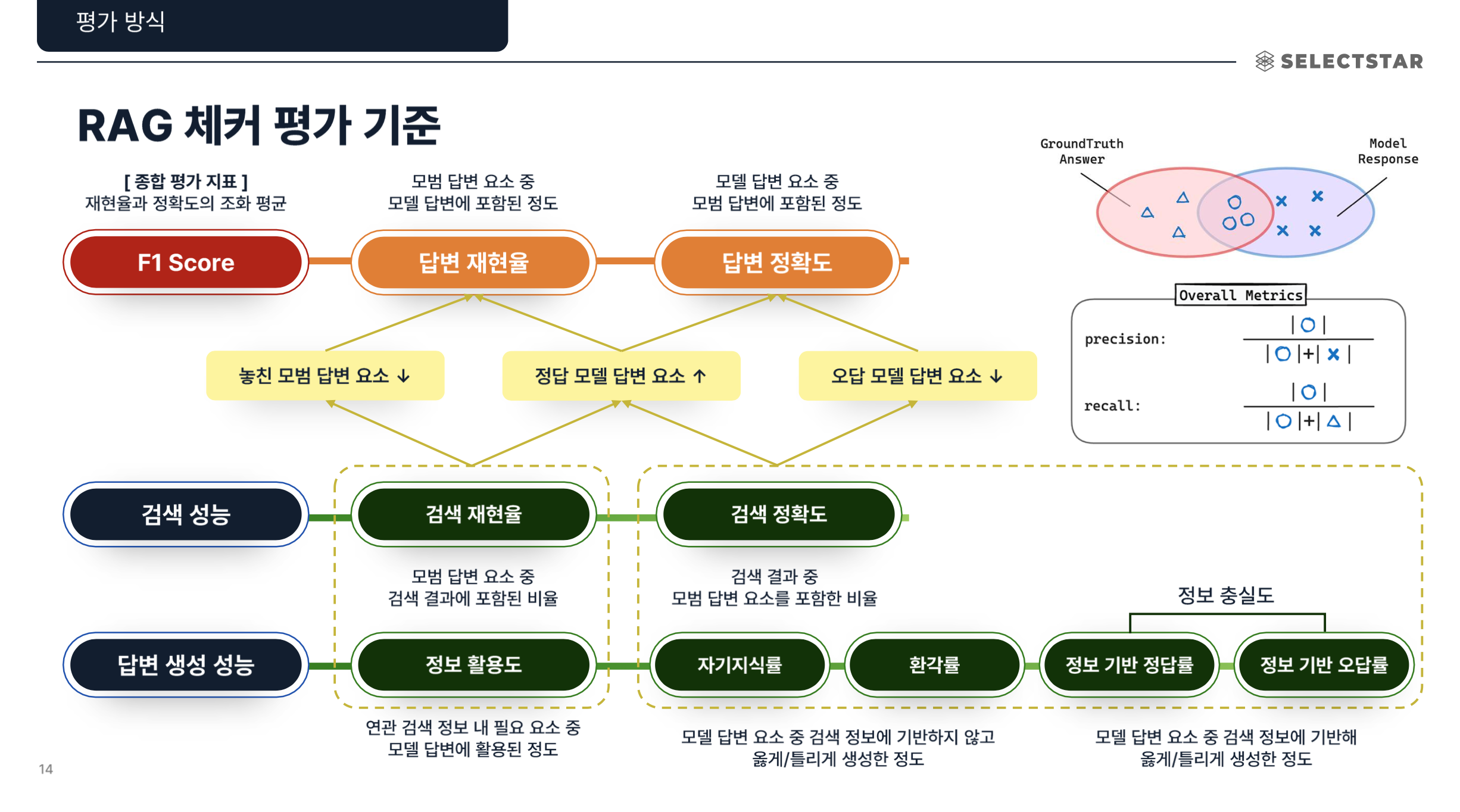
and determines whether each Claim is logically entailed from the retrieved context (Passage) to quantitatively evaluate the Factuality and Performance Diagnosis (Generator / Retriever performance) of the RAG system.
System Components: Internally, it consists of (1) Claim Decomposition Module, (2) Entailment Judge Module, and (3) Metric Aggregator, allowing separate diagnosis of RAG's retrieval and generation stage performance.
Flow (3-step)
-
Decomposition:
- Separates the ER (expected response) and the model's actual response into Claim units.
- Each Claim is defined as a "verifiable fact unit (sentence that can be objectively judged true/false)".
-
Entailment Judgment:
- An LLM Judge determines whether the separated Claims are logically entailed from the retrieved context (Chunk).
-
Metric Aggregation:
- Calculates Overall / Retriever / Generator Metrics based on entailment results.
- Each metric numerically represents the model's accuracy, faithfulness, hallucination rate, context utilization, etc.
Metrics
Glossary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| ER (Expected Response) | The expected answer sentence for evaluation questions (=Ground Truth Answer). |
| Claim | A verifiable fact unit. Decomposes ER and responses into Claim units through LLM for evaluation. |
| Entailment | A logical relationship where a Claim is entailed from context (Passage/Chunk). |
| Chunk / Passage | Document units (context) used as RAG retrieval results. |
| Faithfulness | A metric evaluating whether model responses are based on actual retrieved context. |
| Hallucination | When incorrect information not based on context is generated. |
| Noise Sensitivity | The degree to which a model is influenced by unnecessary information in context to generate incorrect answers. |
| Self-Knowledge | When the model answers correctly using its own knowledge even without retrieved context. |
Strengths & Limitations
Strengths
- Fine-grained metric structure enables stage-by-stage diagnosis of RAG system's Retriever / Generator.
- Compared to qualitative evaluation, claim-level quantitative evaluation ensures reliability and reproducibility.
Limitations
- Evaluation quality depends on the accuracy of Claim Decomposition.
- Does not distinguish Claim importance (core/supplementary information), requiring careful interpretation of Recall/Precision
📄️ Overview
Datumo Eval evaluates RAG systems based on claim-level factuality using ER decomposition and entailment-based verification.
📄️ Run RAG Checker
RAG Checker automatically evaluates a RAG system’s factual accuracy (Factuality) and retrieval–generation performance
📄️ View Report
---
📄️ + Beir Leaderboard
Perform BEIR benchmark evaluation alongside Judge evaluation and check results in the leaderboard.