Query Set
Query Set is a collection of test questions to be presented to the AI model. Unlike other datasets, it can be freely edited until a Response Set is generated, and can be created by uploading a file or automatically generating from a Context Set.
This page guides you through the entire process from creating to editing and managing a Query Set.
- Format: CSV, XLSX
- Structure: Row 1 header (column names), data from row 2 onwards
- Required Column:
query(all others are treated as metadata)
For detailed rules, refer to 📁 Upload Guide below.
3-2-1. Query Generation
Query Set can be created in two ways:
- Method A: Local File Upload
- Method B: AI-Based Generation
If you already have prepared Query data, upload a local CSV/XLSX file to create a Query Set.
- Use pre-defined Queries as-is.
- Suitable for bulk data upload.
Based on registered Context Set, AI automatically generates Queries.
- Basic generation or Custom Prompt application is available.
- Expected Response (ER) generation option is also supported.
3-2-1-1. Local File Upload Generation
① Access Query Set Creation Page
Click the [+ New Query Set] button at the top right.
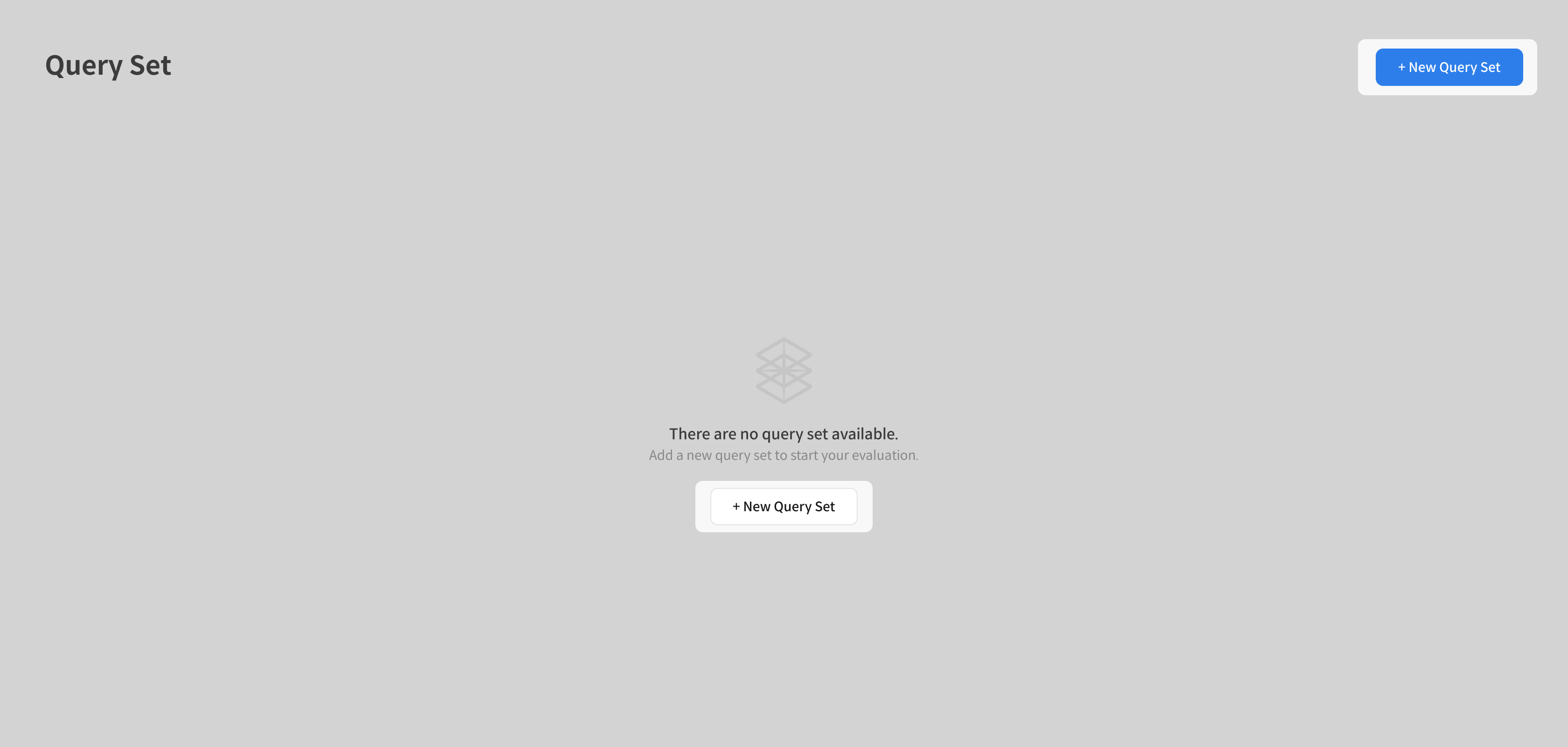
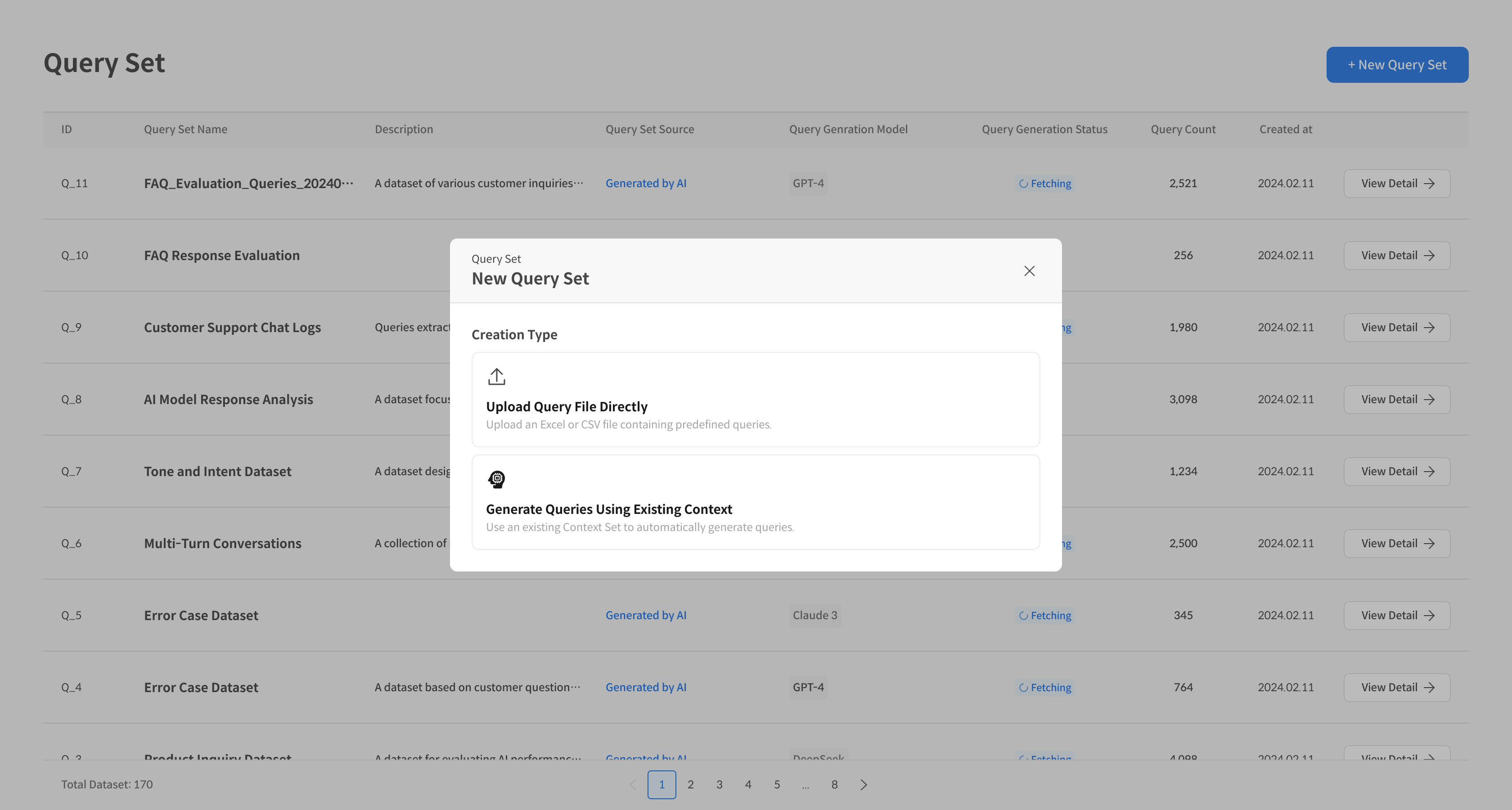
② Select Creation Method
Select [Upload Query File Directly] in the popup window.
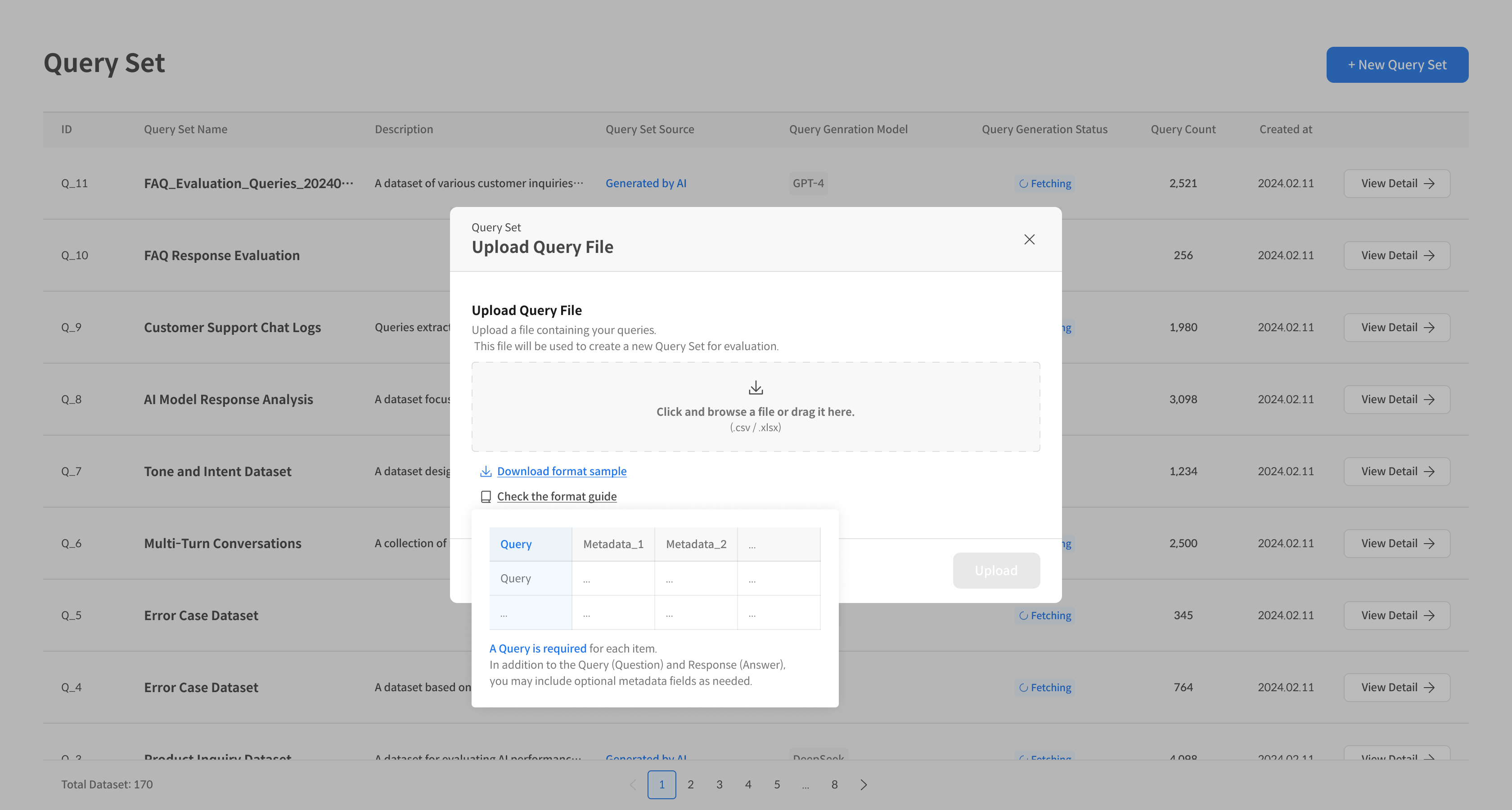
③ Upload File
Click the [Click and browse a file or drag it here] area to select a file or drag to upload.
- Supported formats: CSV, XLSX
- Sample file download available
④ Enter Basic Information
Enter the Query Set name and description (optional).
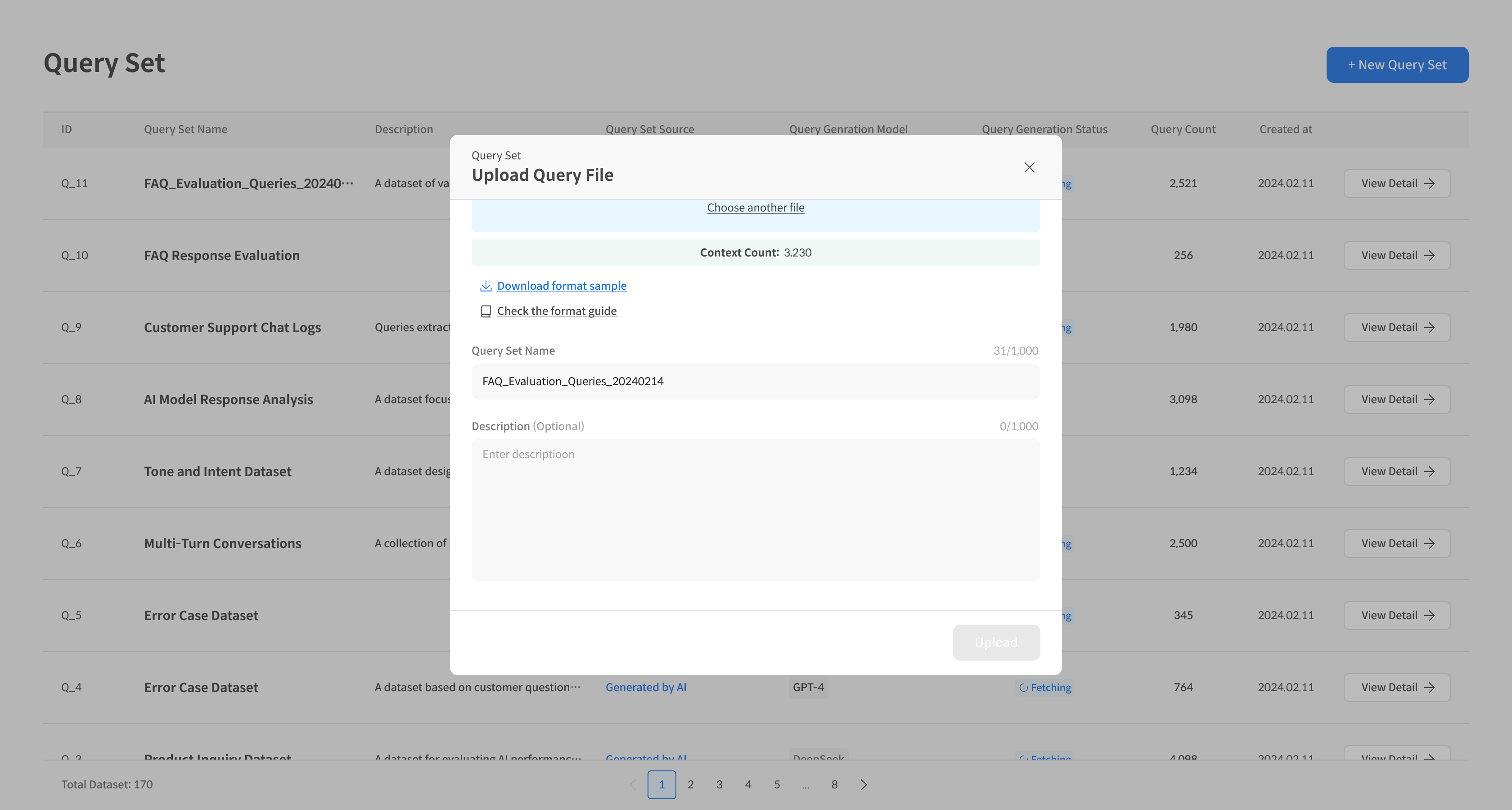
⑤ Save
Click the [Complete] button to save.
3-2-1-2. AI-Based Generation
AI automatically generates Queries based on the Context Set.
- a. Basic Generation
- b. Custom Prompt Generation
- c. Expected Response(ER) Generation
Basic Generation
① Access Query Set Creation Page
Click the [+ New Query Set] button at the top right.

② Select Creation Method
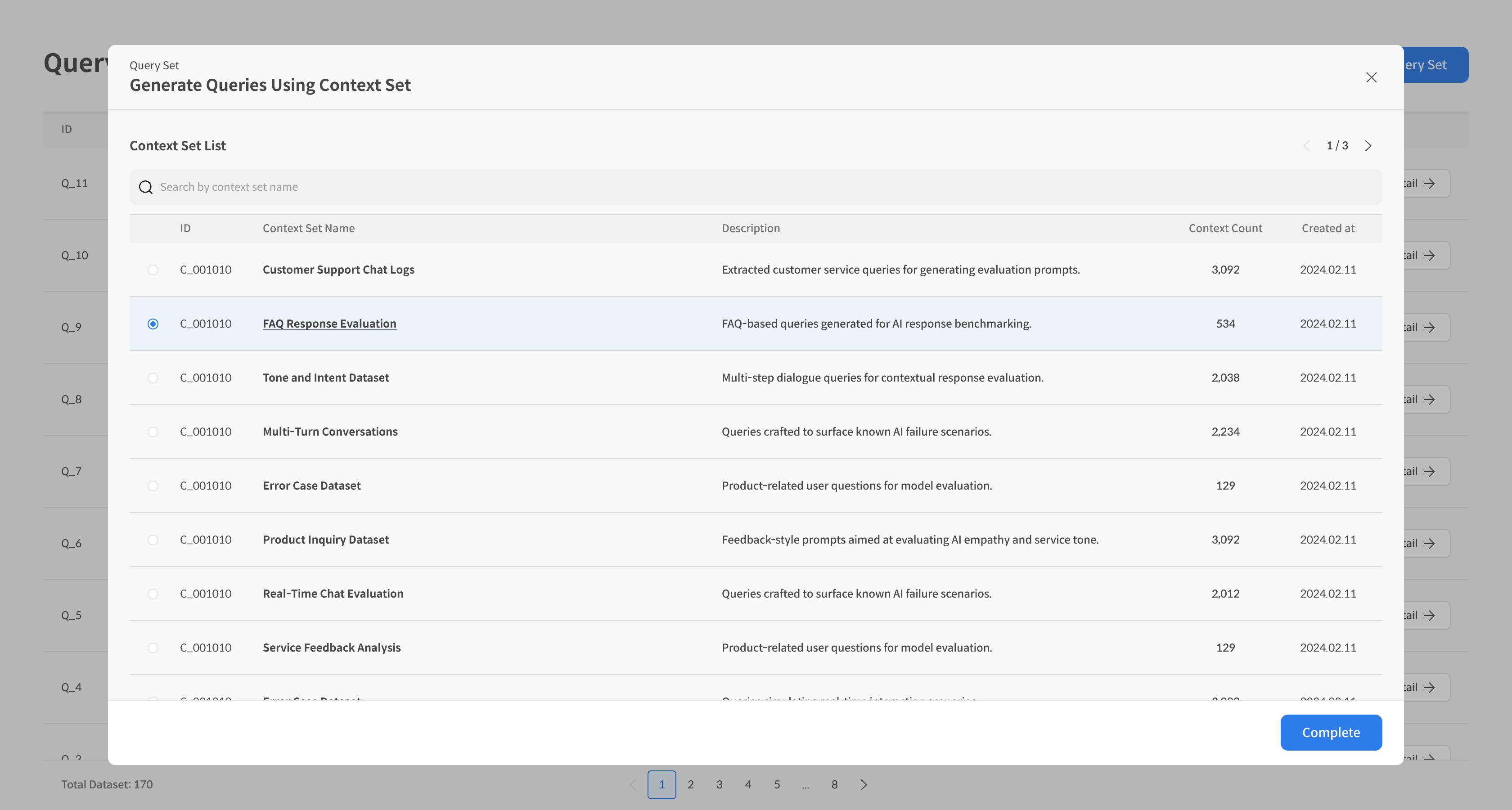
Select a Context Set from the [Generate from Context Set] list.

③ Select Context Set
Select the Context Set to reference when generating questions.
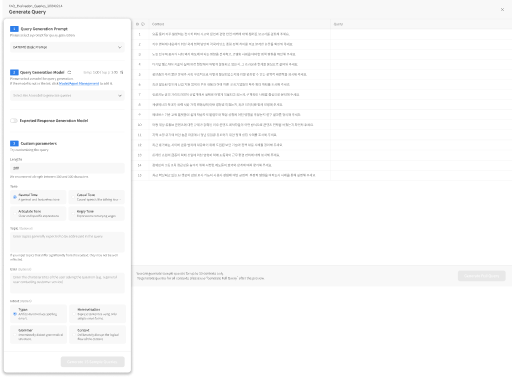
④ Select Query Generation Model
Select the Model/Agent to use for Query generation.
⑤ Set Custom Parameters (Optional)
If necessary, enter Custom Parameters to configure generation conditions in detail.
View parameter details
Each parameter allows you to control the characteristics of generated Queries.
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Length (Sentence Length) | Enter min_length and max_length to control the length of generated Queries | 10-20: "Can I get a refund?"40-60: "I would like to receive a refund for the product I purchased. What process do I need to follow?" |
| Tone (Tone of Voice) | Specifies the style and mood of the Query | Neutral: "What is the delivery timeframe?"Casual: "How long does shipping take?"Angry: "Why is the delivery taking so long!" |
| Topic (Subject) | Limits Queries to a specific topic or category | Entering Shipping-related questions only generates only shipping-related questions |
| User Characteristics | Generates Queries from the perspective of a specific user type | Customer center user → Generates questions in typical customer inquiry format |
| Intent (Intention) | Intentionally includes specific errors or disturbances in Queries. Used for testing AI model robustness. | Typos: "When will my shpiment arrive?"Grammar errors: "Refund want how do I?" |
⑥ Generate Sample Queries
Click the [Generate 15 Sample Queries] button to check samples first. Click the generated Query to check detailed content.
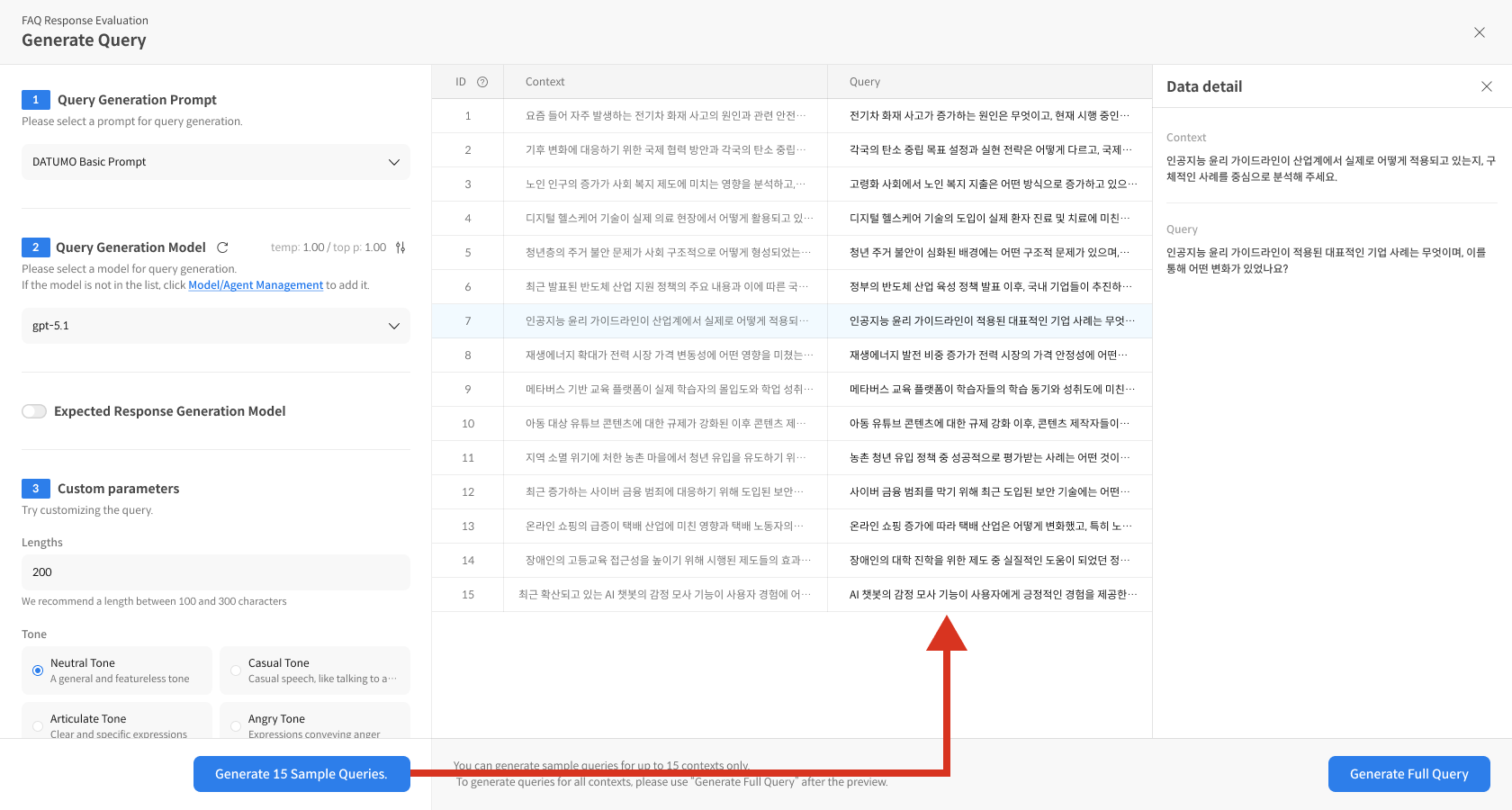
⑦ Generate Full Query
After reviewing the sample, click the [Generate Full Query] button.
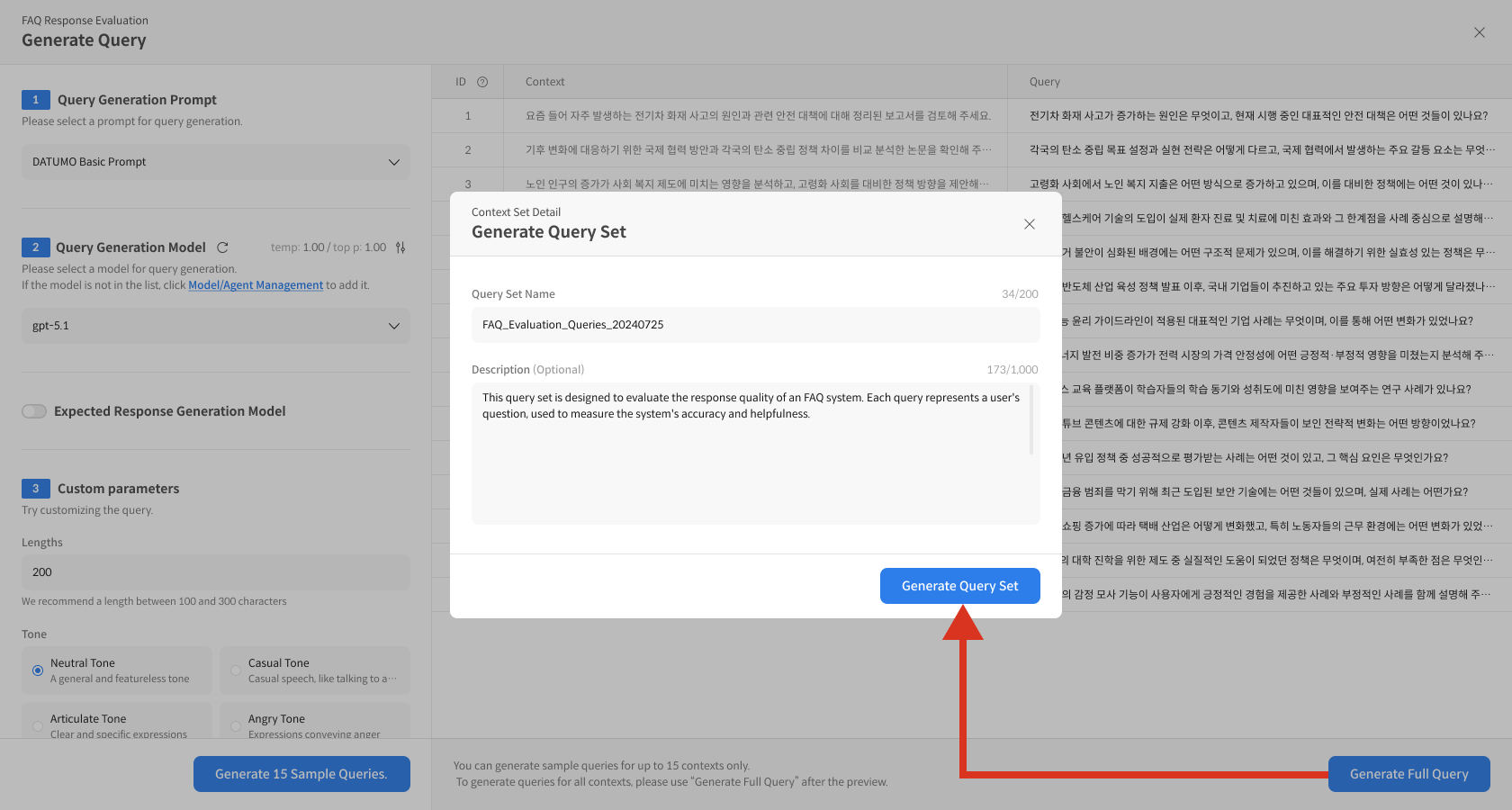
⑧ Enter Basic Information
Enter the Query Set name and description (optional).
⑨ Save
Click the [Generate Query Set] button to save.
Custom Prompt Generation
When creating a Query Set, apply a pre-created Query Generation Custom Prompt to control Query generation more precisely.
- Apply custom prompts instead of basic generation logic
- Advanced settings available including metadata variables, Glossary, Synonym Replacement, etc.
For more details, refer to 👉 Custom Prompt Generation Documentation.
Expected Response(ER) Generation
When creating a Query Set, if Context is available, you can generate Expected Response (ER) together.
- ER can be generated simultaneously with Query generation
- ER can also be generated separately after generation is complete
For more details, refer to 👉 + ER Generation Documentation.
3-2-2. Query Set Management
3-2-2-1. Query Set View
① Check Query Set List
The created Query Set is displayed as a list:
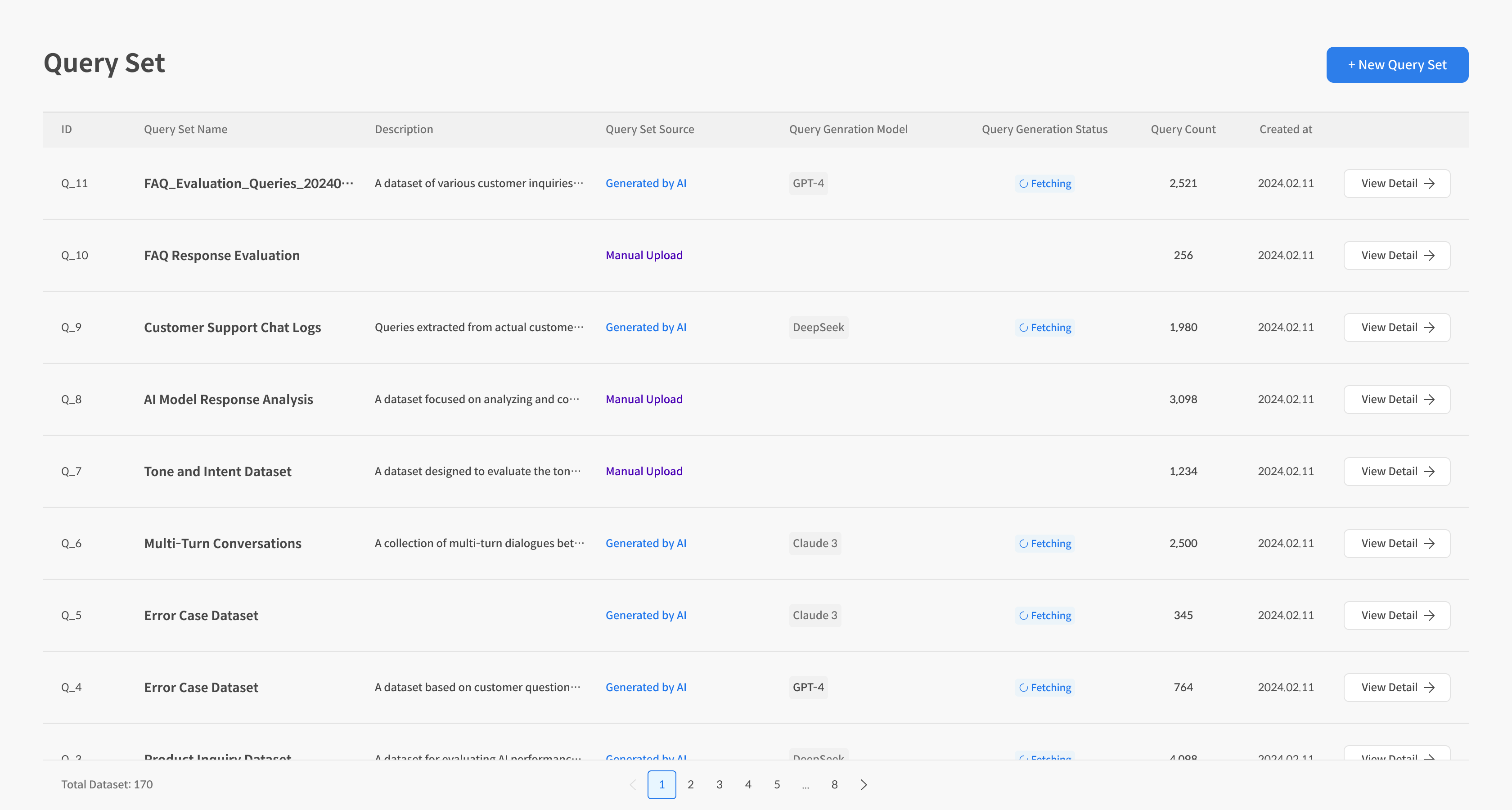
View screen composition items
- Query Set Name: Name of the query set
- Description: Description
- Query Set Source: Distinction between upload/Context-based
- Query Generation Model: Generation model used
- Query Generation Status: Complete/In Progress/Error
- Query Count: Number of questions included
- Created at: Creation date
② Check Query Detailed Information
Click a Query Set from the list to navigate to the detail page. Query data is displayed row by row, and when a specific row is selected, the Data Detail panel on the right shows the Query content and Metadata.

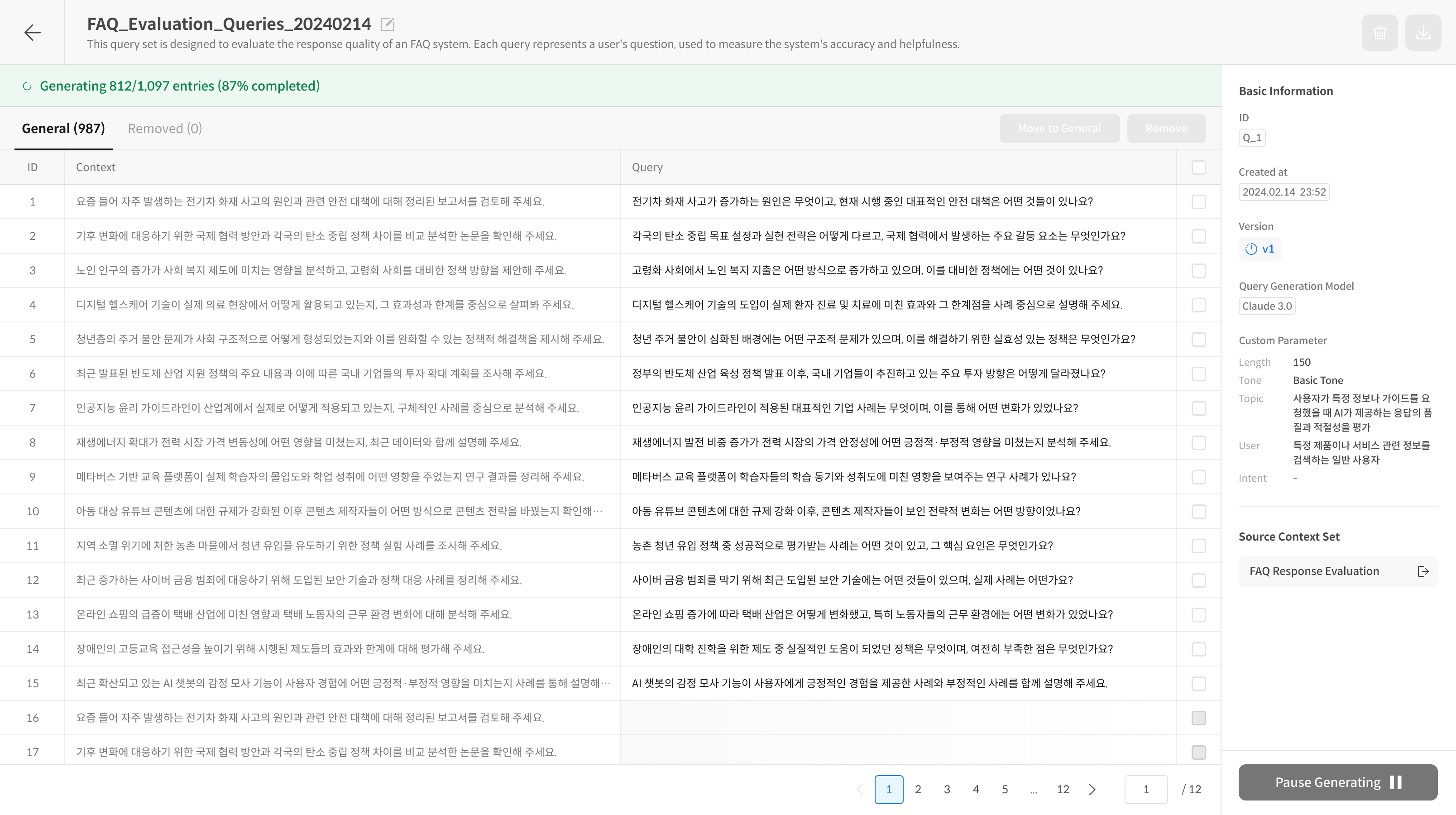
3-2-2-2. Query Set Pause, Restart, Delete
Ongoing Query generation tasks can be controlled from the Query Set detail screen.
① Pause Generation
Click the [Pause] button to temporarily stop the ongoing Query generation.
② Restart Generation
Click the [Restart Generating] button to resume the paused generation task.
③ Delete Query Set
Click the [Delete] button to delete a Query Set that is paused or generation is complete.
Deleted Query Sets cannot be recovered, so caution is required.
3-2-2-3. Query Editing and Modification
Unlike other datasets, the Query Set can be freely modified until a Response Set is generated.
① Edit Query Content (Editing)
Select the Query to modify and click the [Edit] button to directly edit the content.
② Remove Query
Select the checkbox of the Query to exclude and click [Remove].
③ Restore Query (Move to General)
In the Removed tab, select the checkbox of the Query to restore and click [Move to General].
④ Check Modification History (Versioning)
You can check the modification history of each Query based on ID.
3-2-2-4. Query/ER Generation Error Handling
Errors may occur for various reasons during Query or Expected Response (ER) generation. Items with errors are automatically displayed by the system and can be handled in the following ways.
① Check Error Items
When an error occurs during Query or ER generation, check the error items in the Error tab after full generation is complete. Error items are displayed in red status ("Sorry, an Error: (server error message)").
Errors may occur in only one of the Query or Expected Response columns.
② Select Error Handling Method
- Retry All: Retry all error items at once.
- Retry (Individual): Retry only the selected item individually.
- Enter manually: Directly modify Query or ER content.
- Delete: Delete items that are unnecessary or have persistent errors.
- All errors must be resolved to proceed to the next step, Response Set generation.
- If the same error persists, it is recommended to manually input or delete the Query and proceed.
3-2-2-5. Query Set Export
You can export the Query Set being managed to an external file or save it to the platform.
① Export
Click the Export [↑] button at the top.
Export is useful when reusing in other projects or systems after inspection is complete.
📁 Upload Guide
1. Column Summary
| Category | Column Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Required | query | Question content to be used for evaluation |
| Special Columns (Optional) | context | Context referenced when generating the question (= reference_context)※ Not used in evaluation. |
expected_response | Column to be used as the correct answer (Response) → It is convenient to manage by consolidating ground_truth, gt, gold_answer, gold_response, etc. into expected_response.※ Used in RAGAs, BEIR evaluation | |
gold_chunk( gold_context) | Context for verifying the correct answer ※ Used in BEIR evaluation | |
| Other Columns | User-defined (Metadata) | Items other than required/special columns are automatically processed as other columns. |
2. Detailed Description
query: Question content to be used for evaluation (required)context: Context referenced when generating the question (=reference_context) — Not directly used in evaluationexpected_response: Column to be used as the correct answer (same role asground_truth,gt,gold_answer,gold_response, etc.)gold_chunk/gold_context: Context used as the basis for the correct answer during evaluation- Other columns: e.g.,
difficulty,category,source→ Automatically processed as metadata
3. Data Format Example
CSV/XLSX Example
| id | query | category | difficulty | domain |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | What are the customer service hours? | hours | easy | CS |
| 2 | Please explain the refund policy in detail. | policy | medium | Sales |
| 3 | Please tell me the conditions for free shipping. | shipping | easy | Logistics |
⚠️ Precautions
- The
querycolumn must be included. - The first row is recognized as the column name (field name), so enter the header, not data.
- All columns other than required columns are automatically processed as metadata.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q. An error occurred during query generation. How do I handle it?
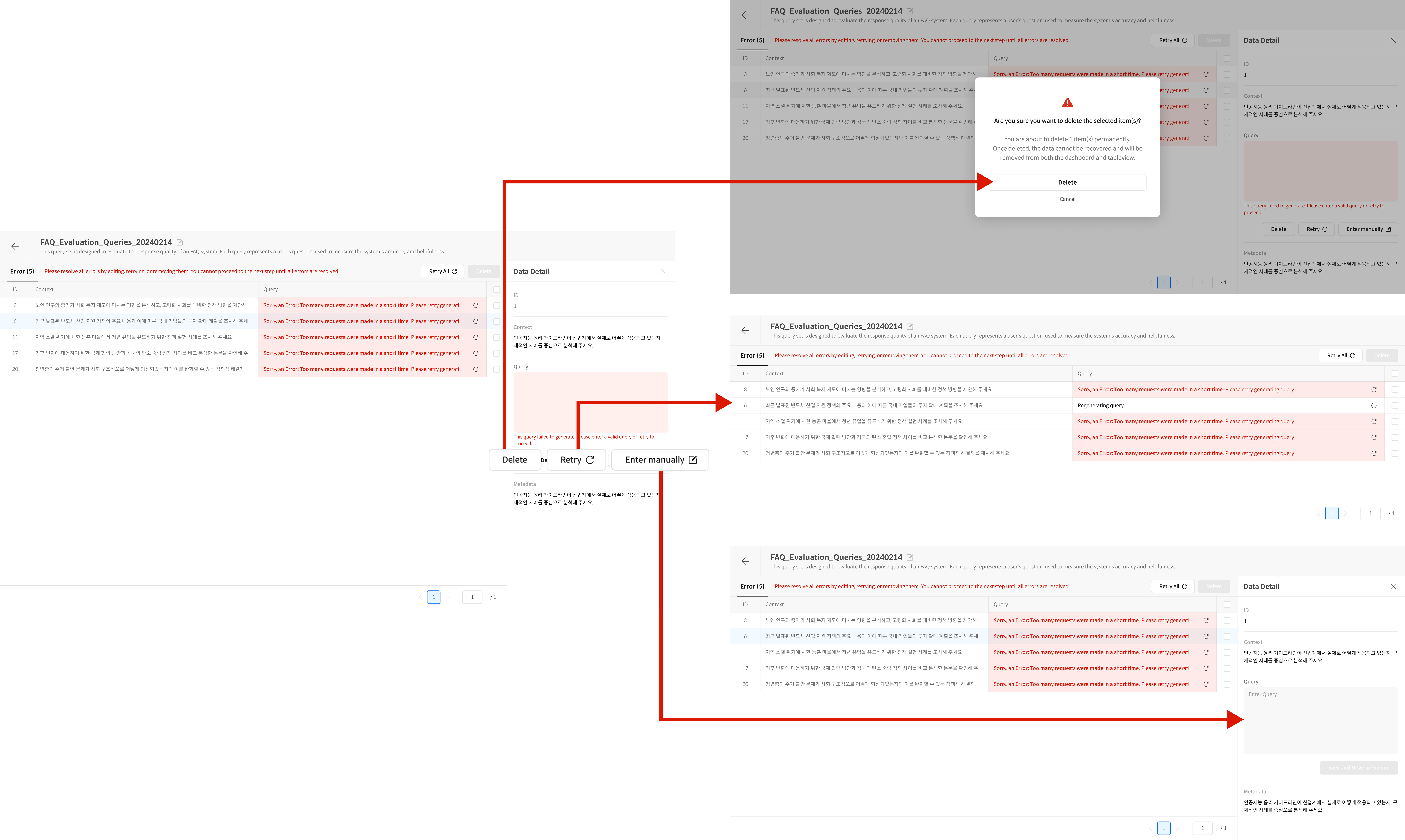
A. When all other query generations are complete, you can check only the items where an error occurred. For error items, you can handle them by choosing one of the following options:
- Delete: Proceed with deletion, excluding the corresponding query
- Retry: Try auto-generation again
- Enter manually: Write the query yourself
You can proceed to the next step after all error cases have been handled.